Modern electrical grids face unprecedented challenges as businesses demand higher reliability, efficiency, and resilience from their power infrastructure. Distribution automation represents a transformative approach that leverages advanced technologies to monitor, control, and optimize electrical distribution systems in real-time. This sophisticated framework integrates intelligent devices, communication networks, and automated control systems to create self-healing grids capable of detecting faults, rerouting power, and maintaining continuous service delivery even during adverse conditions.
The evolution of power distribution systems has accelerated dramatically over the past decade, driven by increasing digitalization and the need for more intelligent grid management. Traditional distribution networks relied heavily on manual operations and reactive maintenance strategies, often resulting in prolonged outages and inefficient power delivery. Today's distribution automation solutions fundamentally change this paradigm by introducing predictive capabilities, automated switching operations, and comprehensive grid visibility that enables utility operators to make informed decisions instantaneously.
Fundamental Components of Distribution Automation Systems
Intelligent Electronic Devices and Sensors
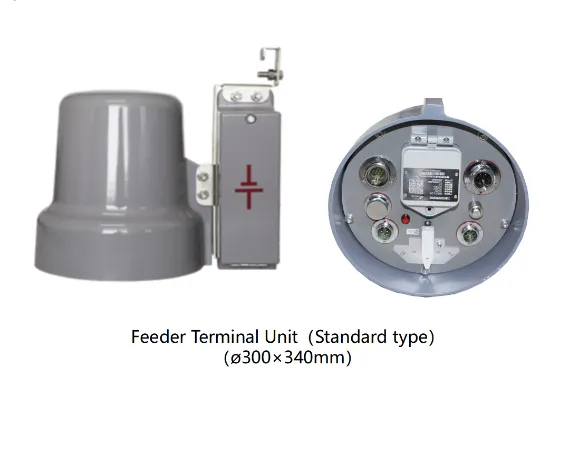
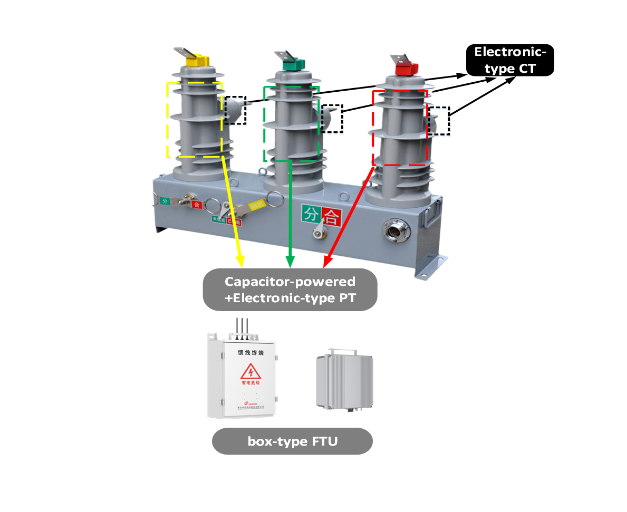
The backbone of any effective distribution automation system consists of strategically deployed intelligent electronic devices that continuously monitor grid conditions and performance parameters. These sophisticated sensors collect real-time data on voltage levels, current flow, power quality metrics, and equipment health indicators across the entire distribution network. Advanced protection relays, smart switches, and automated reclosers work in concert to provide comprehensive situational awareness and enable rapid response to changing grid conditions.
Modern sensor technologies incorporate machine learning algorithms that can identify patterns and anomalies in electrical behavior, predicting potential failures before they occur. This predictive capability allows maintenance teams to schedule interventions proactively, reducing the likelihood of unexpected outages and extending equipment lifespan. The integration of Internet of Things sensors throughout the distribution infrastructure creates a dense monitoring network that provides granular visibility into every aspect of power delivery performance.
Communication Infrastructure and Data Management
Robust communication networks form the nervous system of distribution automation platforms, enabling seamless data exchange between field devices, control centers, and analytical systems. High-speed fiber optic networks, wireless communication protocols, and cellular technologies ensure reliable connectivity even in challenging environmental conditions. This multi-layered communication architecture guarantees that critical operational data reaches control centers without delay, supporting time-sensitive decision-making processes.
Data management systems process vast quantities of information generated by distributed sensors and control devices, applying advanced analytics to extract actionable insights. Cloud-based platforms provide scalable storage and processing capabilities, while edge computing solutions enable localized decision-making that reduces latency and improves system responsiveness. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies enhances the system's ability to learn from historical patterns and optimize operational strategies continuously.
Enhanced Grid Reliability Through Automated Operations
Fault Detection and Isolation Capabilities
One of the most significant advantages of distribution automation lies in its ability to detect and isolate electrical faults within seconds of occurrence. Advanced fault location algorithms analyze electrical signatures and communication patterns to pinpoint the exact location of disturbances, enabling rapid isolation of affected sections while maintaining power delivery to unaffected areas. This precise fault identification capability dramatically reduces the scope of outages and minimizes customer impact during grid disturbances.
Automated isolation systems utilize intelligent switching devices that can operate remotely without requiring field personnel to physically access equipment. These systems evaluate fault conditions in real-time and execute predetermined switching sequences to isolate damaged sections while preserving service to healthy portions of the network. The speed and accuracy of automated fault isolation significantly improve overall grid reliability metrics and reduce the duration of service interruptions.
Self-Healing Grid Capabilities
Self-healing functionality represents the pinnacle of distribution automation technology, enabling grids to automatically reconfigure themselves in response to faults or equipment failures. When a fault occurs, the system immediately analyzes alternative power delivery paths and automatically switches customers to backup feeders or alternate supply routes. This autonomous restoration capability can restore service to most customers within minutes, compared to hours required for manual restoration processes.
The self-healing process involves sophisticated algorithms that consider multiple factors including load balancing, voltage regulation, and equipment capacity constraints when determining optimal restoration strategies. Advanced systems can coordinate multiple switching operations across different voltage levels and geographic areas to achieve comprehensive service restoration while maintaining system stability and power quality standards.
Business Benefits and Economic Impact
Reduced Downtime and Operational Costs
Distribution automation delivers substantial economic benefits through dramatic reductions in outage frequency and duration. Businesses experience fewer interruptions to their operations, translating directly into increased productivity and reduced revenue losses associated with power outages. The automation of routine switching operations and maintenance procedures reduces labor costs while improving operational efficiency across the entire distribution network.
Predictive maintenance capabilities enabled by continuous monitoring significantly reduce equipment failure rates and extend asset lifespans. By identifying potential problems before they result in failures, utilities can schedule maintenance activities during planned outage windows, minimizing customer impact while optimizing maintenance resource allocation. This proactive approach typically reduces maintenance costs by twenty to thirty percent while improving overall system reliability.
Improved Power Quality and Voltage Regulation
Automated voltage regulation systems continuously adjust voltage levels throughout the distribution network to maintain optimal power quality for all customers. Advanced voltage control algorithms coordinate the operation of voltage regulators, capacitor banks, and distributed energy resources to ensure consistent voltage levels regardless of load variations or system disturbances. This precise voltage control reduces energy losses and protects sensitive customer equipment from voltage-related damage.
Power quality monitoring systems identify and address harmonic distortion, voltage fluctuations, and other power quality issues that can affect business operations. Real-time correction capabilities ensure that power delivered to customers meets stringent quality standards required by modern industrial processes and sensitive electronic equipment. Enhanced power quality translates into improved equipment performance, reduced maintenance costs, and increased operational efficiency for business customers.
Integration with Renewable Energy Sources
Distributed Energy Resource Management
Distribution automation systems play a crucial role in managing the integration of renewable energy sources such as solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems. Advanced control algorithms coordinate the output of distributed energy resources with grid demand patterns, optimizing the utilization of clean energy while maintaining system stability. This intelligent coordination enables higher penetration levels of renewable energy without compromising grid reliability or power quality.
Energy storage integration through distribution automation platforms provides additional flexibility and resilience to the power grid. Battery storage systems can be automatically dispatched during peak demand periods or grid emergencies, providing backup power and grid stabilization services. The coordination of multiple storage systems across the distribution network creates a virtual power plant capable of providing grid services equivalent to traditional generating facilities.
Microgrid Coordination and Island Operation
Advanced distribution automation enables seamless coordination between the main grid and microgrid installations, supporting both grid-connected and islanded operation modes. During normal conditions, microgrids operate in parallel with the main distribution system, contributing renewable energy and providing local load support. When grid disturbances occur, automated systems can seamlessly transition microgrids to island mode, maintaining power delivery to critical loads using local generation and storage resources.
The ability to coordinate multiple microgrids and distributed energy resources creates opportunities for peer-to-peer energy trading and localized energy markets. Distribution automation platforms facilitate these transactions by managing power flows, monitoring energy quality, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. This emerging capability enables new business models and revenue streams while improving overall grid resilience and sustainability.
Future Developments and Technology Trends
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
The future of distribution automation lies in the deeper integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies that can analyze complex patterns in grid behavior and optimize operations autonomously. Advanced AI algorithms will enhance predictive capabilities, enabling more accurate forecasting of equipment failures, load demands, and optimal maintenance schedules. These intelligent systems will continuously learn from operational experience, improving their performance and decision-making capabilities over time.
Machine learning applications in distribution automation include advanced fault prediction models, dynamic load forecasting systems, and automated optimization algorithms that can adapt to changing grid conditions in real-time. These technologies will enable more sophisticated control strategies that consider multiple objectives simultaneously, including reliability, efficiency, environmental impact, and economic optimization. The evolution toward fully autonomous grid management represents the ultimate goal of distribution automation development.
Edge Computing and Real-Time Analytics
Edge computing technologies are revolutionizing distribution automation by enabling real-time data processing and decision-making at the network edge, closer to where data is generated. This distributed computing approach reduces communication latency, improves system responsiveness, and enables more sophisticated local control strategies. Edge-based analytics can process streaming data from sensors and control devices to identify patterns and anomalies that might be missed by centralized systems.
The deployment of edge computing platforms throughout the distribution network creates a mesh of intelligent nodes capable of coordinating local operations while maintaining connectivity to central control systems. This architecture enhances system resilience by enabling continued operation even when communication with central facilities is disrupted. Advanced edge analytics will support more granular control strategies and enable new applications such as real-time optimization of distributed energy resources and dynamic pricing mechanisms.
FAQ
What are the primary components required for implementing distribution automation
Distribution automation implementation requires several key components including intelligent electronic devices such as smart switches and protective relays, communication infrastructure for data transmission, supervisory control and data acquisition systems for centralized monitoring, and advanced analytics software for processing operational data. The system also needs robust cybersecurity measures, redundant communication pathways, and integration capabilities with existing utility management systems to ensure seamless operation and maximum effectiveness.
How does distribution automation improve response times during power outages
Distribution automation dramatically improves outage response times by enabling automatic fault detection, isolation, and service restoration without requiring manual intervention. Advanced systems can identify fault locations within seconds, automatically isolate affected sections, and restore service to unaffected customers through alternative power paths. This automated response capability can restore service to most customers within minutes compared to traditional manual processes that may require hours to complete, significantly reducing the overall impact of power disturbances.
What cybersecurity considerations are important for distribution automation systems
Cybersecurity is critical for distribution automation systems due to their reliance on digital communication networks and control systems. Essential security measures include encrypted communication protocols, multi-factor authentication systems, network segmentation to isolate critical control functions, regular security audits and vulnerability assessments, and comprehensive incident response procedures. Utilities must also implement robust access controls, maintain updated security patches, and ensure compliance with industry cybersecurity standards such as NERC CIP requirements for grid security.
How can businesses justify the investment costs associated with distribution automation
The investment in distribution automation can be justified through multiple economic benefits including reduced outage costs, improved operational efficiency, extended equipment lifespans, and enhanced power quality that reduces equipment damage and maintenance expenses. Studies typically show that distribution automation systems pay for themselves within three to five years through reduced operational costs and improved reliability metrics. Additional benefits include improved customer satisfaction, compliance with regulatory reliability standards, and enhanced capability to integrate renewable energy sources that can provide long-term economic advantages.
Table of Contents
- Fundamental Components of Distribution Automation Systems
- Enhanced Grid Reliability Through Automated Operations
- Business Benefits and Economic Impact
- Integration with Renewable Energy Sources
- Future Developments and Technology Trends
-
FAQ
- What are the primary components required for implementing distribution automation
- How does distribution automation improve response times during power outages
- What cybersecurity considerations are important for distribution automation systems
- How can businesses justify the investment costs associated with distribution automation







