Modern electrical power distribution networks face increasing complexity as utility companies strive to deliver reliable, efficient, and cost-effective energy services to their customers. The integration of advanced technologies has revolutionized how electrical systems operate, with distribution automation systems emerging as a critical component for enhancing grid performance and reliability. These sophisticated platforms combine intelligent monitoring, control, and communication capabilities to transform traditional distribution networks into smart, responsive infrastructure that can adapt to changing conditions in real-time.
The implementation of distribution automation systems represents a paradigm shift from reactive maintenance and manual operations to proactive, data-driven management of electrical distribution networks. This transformation enables utility companies to optimize their operations, reduce operational costs, and significantly improve service quality for end consumers. Understanding the comprehensive advantages of these systems is essential for organizations considering modernization of their electrical infrastructure.
Enhanced System Reliability and Performance
Real-Time Monitoring and Fault Detection
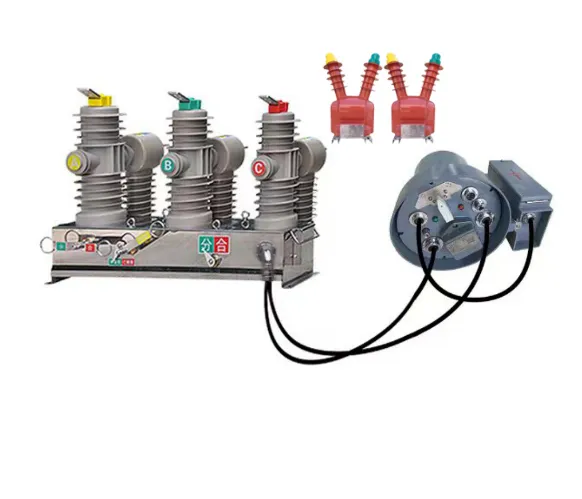
Distribution automation systems provide continuous monitoring of electrical parameters throughout the network, enabling immediate detection of abnormal conditions, equipment failures, and potential safety hazards. Advanced sensors and communication technologies collect real-time data on voltage levels, current flow, power quality metrics, and equipment status, transmitting this information to centralized control centers for analysis and response. This comprehensive monitoring capability allows operators to identify problems before they escalate into major outages or equipment damage.
The sophisticated fault detection algorithms incorporated into these systems can distinguish between temporary disturbances and permanent faults, automatically initiating appropriate response procedures. When faults occur, the system can rapidly isolate affected areas while maintaining power supply to unaffected customers, significantly reducing the scope and duration of outages. This intelligent fault management capability is particularly valuable in urban areas where high customer density makes service interruptions especially costly and disruptive.
Automated Switching and Load Management
Modern distribution automation systems incorporate sophisticated switching capabilities that enable automatic reconfiguration of the electrical network in response to changing conditions or equipment failures. Automated switches, controlled by intelligent algorithms, can reroute power flows to bypass damaged equipment or redistribute loads to prevent overloading of critical infrastructure components. This dynamic reconfiguration capability ensures optimal utilization of available capacity while maintaining system stability.
Load management features within these systems enable utilities to balance supply and demand more effectively, particularly during peak consumption periods or when renewable energy sources are experiencing fluctuations. Intelligent load shedding and demand response programs can be automatically implemented to maintain system stability while minimizing customer impact. These capabilities are becoming increasingly important as electrical grids integrate higher levels of variable renewable energy sources and electric vehicle charging infrastructure.
Operational Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Reduced Maintenance Requirements
The predictive maintenance capabilities enabled by distribution automation systems represent a significant advancement over traditional time-based maintenance schedules. Continuous monitoring of equipment condition parameters allows maintenance teams to identify developing problems before they result in failures, enabling proactive replacement or repair of components when convenient rather than during emergency situations. This approach reduces both direct maintenance costs and the indirect costs associated with unplanned outages.
Advanced analytics algorithms process historical and real-time data to establish baseline performance patterns for each piece of equipment, identifying deviations that may indicate impending failures. This data-driven approach to maintenance scheduling optimizes resource allocation, reduces inventory requirements for spare parts, and extends the operational life of expensive infrastructure components. The resulting improvements in asset utilization and maintenance efficiency translate directly into reduced operational costs for utility companies.
Improved Workforce Productivity
Distribution automation systems significantly enhance workforce productivity by providing field personnel with accurate, real-time information about system conditions and equipment status. Mobile communication capabilities enable technicians to receive detailed fault location information, equipment specifications, and safety precautions before arriving at job sites, reducing troubleshooting time and improving first-time fix rates. This enhanced information flow eliminates much of the guesswork traditionally associated with electrical system maintenance and repair.
The centralized control capabilities of these systems also reduce the need for personnel to travel to remote locations for routine switching operations or data collection activities. Remote operation of switches, voltage regulators, and capacitor banks can be performed from control centers, freeing field crews to focus on more complex maintenance and construction activities. This improved resource allocation enables utilities to maintain service quality with smaller crews while reducing vehicle fleet requirements and associated operating costs.
Customer Service Enhancement
Faster Outage Response and Restoration
Distribution automation systems dramatically improve outage response times through automated fault detection and precise fault location capabilities. When outages occur, these systems immediately identify the affected area, determine the likely cause of the problem, and provide dispatchers with detailed information needed to coordinate repair efforts. This rapid response capability reduces customer minutes interrupted and improves overall service reliability metrics that are increasingly important for regulatory compliance and customer satisfaction.
The automated switching capabilities of these systems enable partial service restoration in many cases, allowing power to be restored to unaffected customers within minutes of an outage while repair crews work to address the underlying problem. This selective restoration capability is particularly valuable for critical customers such as hospitals, emergency services, and industrial facilities that cannot tolerate extended power interruptions. The improved outage management provided by distribution automation systems helps utilities maintain competitive advantage in deregulated markets where customer choice drives business success.
Enhanced Power Quality Management
Modern electrical loads, particularly sensitive electronic equipment and industrial processes, require consistent, high-quality electrical supply to operate reliably. Distribution automation systems incorporate voltage regulation and power quality monitoring capabilities that ensure consistent delivery of electricity within acceptable parameters. Automated voltage regulators and capacitor banks respond to changing load conditions to maintain optimal voltage levels throughout the distribution network.
Power quality disturbances such as voltage sags, surges, and harmonic distortion can be automatically detected and analyzed to identify their sources and impacts on customer equipment. This information enables utilities to take corrective action to prevent recurring problems and provides valuable data for addressing customer complaints about power quality issues. The proactive power quality management enabled by distribution automation systems reduces customer equipment damage and improves satisfaction with utility services.
Integration with Renewable Energy Sources
Managing Distributed Generation
The increasing deployment of distributed renewable energy sources such as solar panels and wind turbines creates new challenges for electrical distribution networks. Distribution automation systems provide the monitoring and control capabilities needed to safely integrate these variable generation sources while maintaining system stability and power quality. Real-time monitoring of distributed generation output enables automatic adjustment of voltage regulation equipment and protective device settings to accommodate changing generation patterns.
Advanced communication capabilities allow distribution automation systems to coordinate with distributed generation systems to optimize overall network performance. During periods of high renewable generation, excess energy can be automatically directed to energy storage systems or used to serve loads in adjacent areas through dynamic network reconfiguration. This intelligent management of distributed resources maximizes the value of renewable energy investments while maintaining system reliability and power quality standards.
Grid Modernization and Smart Grid Integration
Distribution automation systems serve as the foundation for broader smart grid initiatives that promise to transform the electrical power industry. These systems provide the communication infrastructure and data collection capabilities needed to implement advanced applications such as demand response programs, dynamic pricing, and electric vehicle integration. The standardized communication protocols used in modern distribution automation systems enable seamless integration with other smart grid technologies and applications.
The data collected by distribution automation systems provides valuable insights into customer consumption patterns, network performance characteristics, and equipment condition trends that inform strategic planning decisions. This information enables utilities to optimize their investment strategies, prioritize infrastructure upgrades, and develop new service offerings that meet evolving customer needs. The scalable architecture of modern distribution automation systems ensures that initial investments can be expanded and enhanced as smart grid technologies continue to evolve.
Regulatory Compliance and Environmental Benefits
Meeting Performance Standards
Utility companies face increasingly stringent regulatory requirements for service reliability, environmental performance, and customer satisfaction. Distribution automation systems provide the monitoring and reporting capabilities needed to demonstrate compliance with these requirements while improving actual performance metrics. Automated data collection eliminates the manual processes traditionally used for regulatory reporting, reducing administrative costs while improving data accuracy and timeliness.
The improved outage management and power quality provided by distribution automation systems directly supports compliance with reliability standards such as those established by the North American Electric Reliability Corporation and similar organizations worldwide. Detailed event logging and analysis capabilities enable utilities to identify and address systemic issues that could lead to regulatory violations or customer service problems.
Environmental Impact Reduction
Distribution automation systems contribute to environmental sustainability through improved energy efficiency and reduced carbon emissions. Optimized voltage regulation reduces energy losses in distribution networks, while improved load management capabilities enable better integration of renewable energy sources. The reduced need for vehicle trips to perform manual switching operations and data collection activities also contributes to lower fuel consumption and emissions.
The enhanced monitoring capabilities of these systems enable utilities to identify and address energy losses more effectively, improving overall system efficiency. Predictive maintenance capabilities reduce waste associated with premature equipment replacement while extending asset life, contributing to more sustainable resource utilization. These environmental benefits are becoming increasingly important as utilities work to meet carbon reduction goals and support broader sustainability initiatives.
FAQ
How long does it typically take to implement distribution automation systems
Implementation timelines for distribution automation systems vary significantly depending on the scope and complexity of the project. Small-scale deployments covering a few distribution circuits can be completed in 6-12 months, while comprehensive system-wide implementations may require 3-5 years to complete. The timeline depends on factors such as existing infrastructure condition, communication system requirements, integration with legacy systems, and regulatory approval processes. Most utilities adopt a phased implementation approach, prioritizing critical circuits and high-impact areas first while gradually expanding coverage across their service territory.
What are the typical return on investment periods for these systems
Return on investment for distribution automation systems typically ranges from 5-10 years, depending on the specific benefits realized and local economic conditions. The primary financial benefits include reduced outage costs, improved operational efficiency, deferred infrastructure investments, and enhanced customer satisfaction leading to reduced customer churn in competitive markets. Utilities with high outage costs or aging infrastructure often see faster payback periods, while those with already reliable systems may focus on operational efficiency and future-proofing benefits that provide longer-term value.
How do distribution automation systems impact cybersecurity requirements
Distribution automation systems introduce additional cybersecurity considerations due to their increased connectivity and data exchange capabilities. Modern systems incorporate multiple layers of security including encrypted communications, authentication protocols, network segmentation, and intrusion detection systems. Utilities must develop comprehensive cybersecurity programs that address both operational technology and information technology domains, including regular security assessments, incident response procedures, and staff training programs. While cybersecurity requirements add complexity and cost, properly implemented security measures ensure that the benefits of automation can be realized without compromising system integrity.
What training requirements are needed for operating personnel
Operating personnel require comprehensive training on both the technical aspects of distribution automation systems and the operational procedures for using these systems effectively. Training programs typically include system architecture, communication protocols, human-machine interface operation, alarm management, and emergency response procedures. Field personnel need additional training on remote-controlled equipment operation and safety procedures for working with automated systems. Most vendors provide initial training programs, but utilities should also develop ongoing training initiatives to keep pace with system updates and ensure consistent operational practices across all shifts and personnel.







